Having a slow computer can be frustrating and even dangerous at times. Therefore, you should always be careful of your CPU usage. Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation is one of them. You can find out if this process is causing you issues by checking the Task Manager and identifying the process. Are you sure that your CPU usage is unusually high because of this Windows process? Read our article to find out how to stop the high usage issue, whether or not it’s dangerous, and what the process is.
Overview of Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation
Isolation Overview Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation (or WADGI) is an application that enables you to isolate audio devices and use only one of them at a time. It will make your computer faster and more stable. This process is important for computers with low memory. Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation is a feature of Windows 10 Pro, and it requires a minimum of 512MB of RAM. If you’re using an older version of Windows, you can try to install the latest version of WADGI. It will not harm your computer. Isolation Basics If you’re having issues with your computer’s performance, you should try to stop WADGI.
How Come It Consumes So Many System Resources Sometimes?
There are a lot of audio enhancement drivers that have a tendency to consume too many system resources, consume your CPU or memory, or even thrash your hard drive. You should be able to see “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” using 0% of your CPU, minimal memory, and no disk activity. These numbers may spike when audio effects are applied, but not much, and they should quickly return to the baseline. If you see “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” routinely using more of any of these three resources, then you may have a problem.
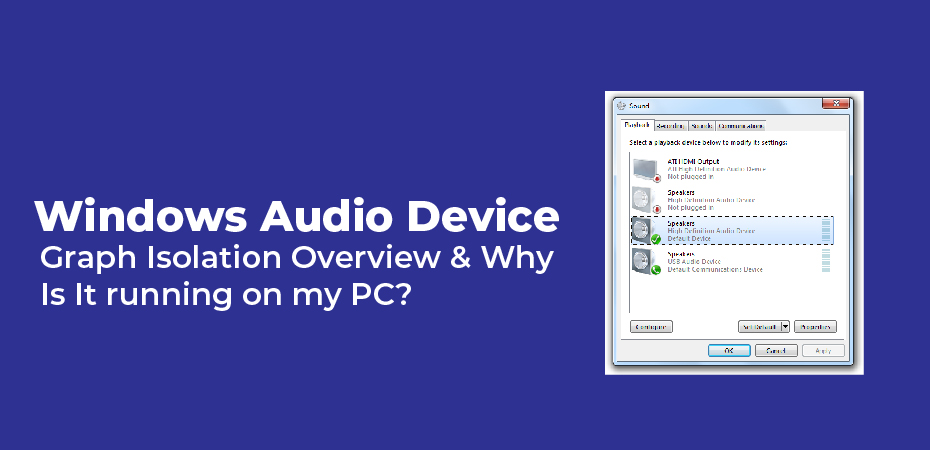
You can also resolve the problem by disabling the effects, but you may have to do that on a device-by-device basis. In Windows, you can open up the Sound properties dialog by right-clicking the speaker icon in your Notification area and then clicking “Sound.” You can also open up your Control Panel and run the Sound applet there. Same thing. On the “Playback” tab of the “Sound” window, select the device that you suspect may be causing issues and then click “Properties.
If you’re looking at a device built into a computer, you’ll see a list of the enhancements available on the device. This list will vary depending on the device you’re using. Start by selecting the “Disable all enhancements” option and see if that resolves your problem. If disabling all the enhancements does fix the problem, you know you’re on the right track, and you can go back and try disabling each specific enhancement, in turn, to narrow down the cause. If you are having problems with your device, you should disable all enhancements to see if that helps.
How do I disable it?
The “Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation” can’t be disabled without also disabling the leading Windows Audio service, and disabling them wouldn’t accomplish much other than making your computer soundless. There is no way to end the process temporarily. Windows will ask you if you want to open the Audio Troubleshooter instead if you attempt to do so.
It wouldn’t hurt to run through the troubleshooter. Of course, if you have already disabled enhancements, it may not solve your problem, but you never know. The troubleshooters are also accessible by clicking Start, typing “troubleshooting,” and pressing Enter.